ETRI® ELECTRONIC TRIAGE –When Minutes Count™
Triage
- Triage is the process of determining a person’s health needs and priority based on a series of questions and answers.
- Triage is the first point of contact with the emergency department.
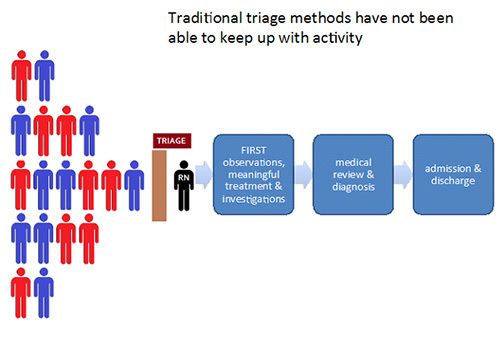
- Triage is currently a manual process that is highly variable, inefficient, unsafe and unsustainable for the current demand of the community.
- Over the past 5 years, the increase in demand for the emergency department has been twice that of population growth.
Staff
- Triage is performed by senior and highly skilled clinicians.
- The high demand on triage often places highly skilled clinicians predominantly in a data entry capacity.
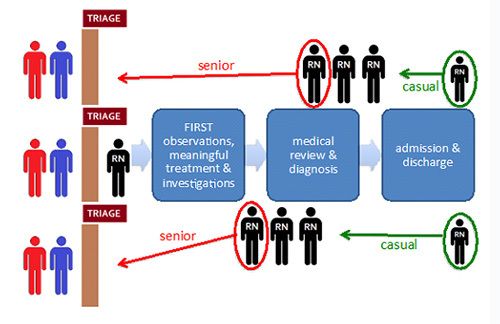
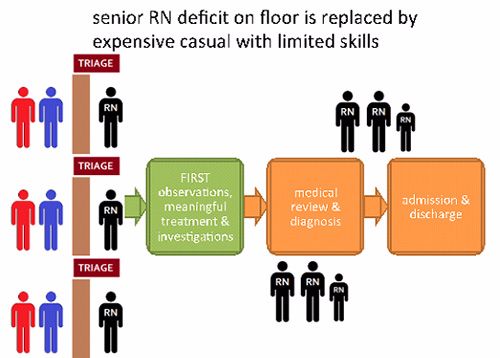
- Highly skilled staff are often absorbed from other duties in the emergency department to keep up with triage demand, negatively impacting the skill mix of the rest of the emergency department.
- Casual staff who temporarily replace senior clinicians are expensive, with limited skills negatively impacting flow.
Patients
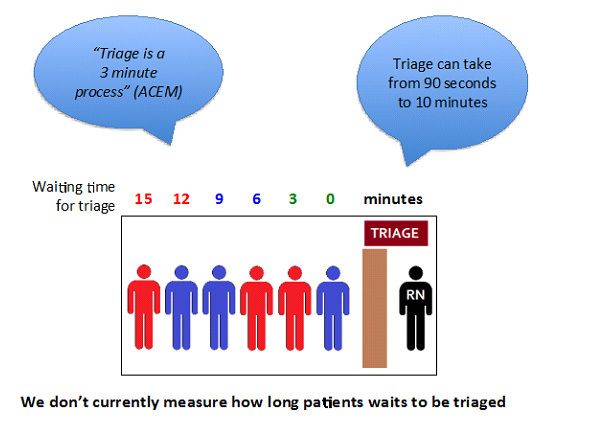
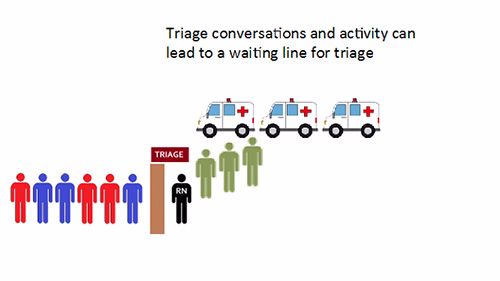
- During peak periods, individual triage conversations between patient and clinician can often lead to triage waiting lines.
- High demand for triage processing can often lead to a delay in the commencement of meaningful treatment.
- Delays to triage or meaningful treatment can be a risk to patient safety and lead to an inefficient patient journey.
Flow
- Delays secondary to one-on-one manual triage processes, can delay the flow of urgent attention being delivered to patients in need.
- A delay in meaningful treatment commenced at triage, can delay the flow of the patient through other stages of the emergency department.
- When the triage process is not working efficiently, clinical decision-making can be delayed, impacting flow.
- A higher concentration of senior staff at triage can negatively impact the flow of patients through the emergency department.
Data
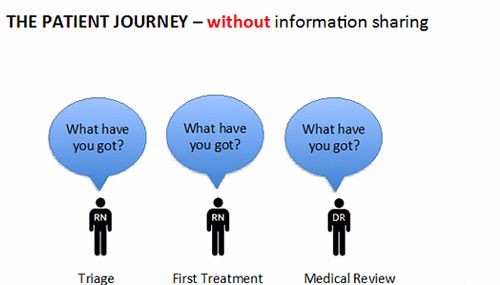
- While the verbal process of triage is broadly the same, the level of information noted between staff is often inconsistent.
- Most emergency information systems contain free text fields for triage that promote highly variable triage data collection.
- Inconsistency and variability often depends on triage staff, level of urgency and business of triage workload.
- Data inconsistency leads to a duplication of effort and the patient being asked the same questions repeatedly, as well as other inefficiencies.
- Inconsistent triage data is impossible to analyse with value.
Cost
- Current methods of managing “pre-load” (excessive patients arriving in a short period needing triage) are expensive and inefficient.
- Ambulance delays related to triage inefficiencies are costly.
- Delays in identifying patient’s needing more urgent care can be costly.
- An ever-increasing need for the short-term reallocation of senior staff to focus on triage instead of maintaining flow, can lead to costly preventable patient deterioration due to delayed decision making.